LED – Light Emitting Diode
LEDs are electronic devices. When current flows through the diode in the pass-through direction, it emits light.
The LED was invented in 1956, and has been in industrial use since 1970. However, until recently red, yellow and green LEDs were mainly used.
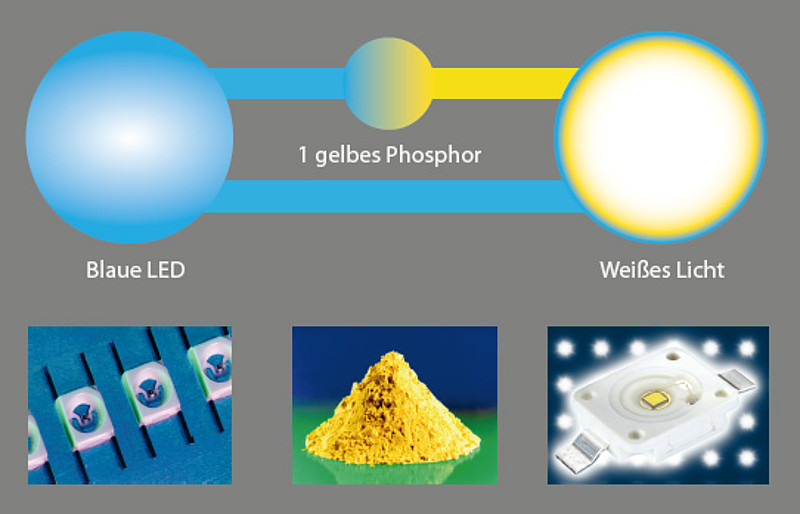
White LEDs were introduced in 1995. They are manufactured by luminescence conversion. In this process, a blue LED is coated with yellow phosphor in order to produce white light. The amount of phosphor influences the color temperature. The thicker the phosphor layer, the warmer the light.
Benefits of LEDs
- Very low power consumption
- Low heat generation
- Long life (up to 60,000 hours)
- Low maintenance cost
- Mercury-free
- No UV radiation
- Small design
- Precise light guidance
- Very good color rendering properties

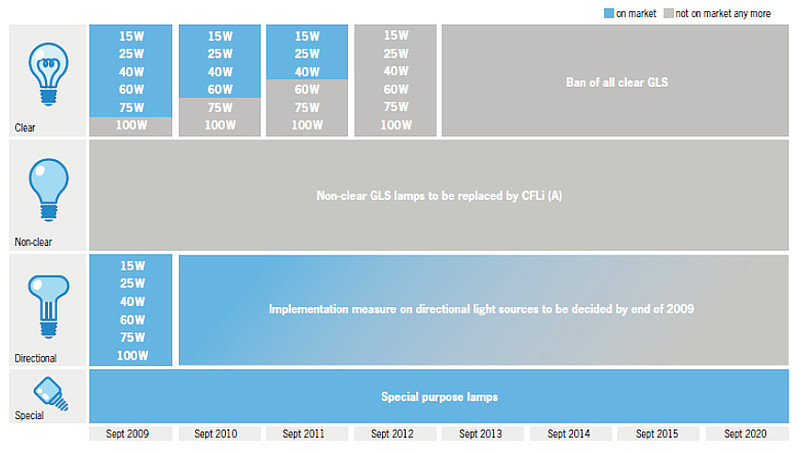
Bulb replacement
In September 2009, 100 W bulbs were withdrawn from the market EU-wide
In September 2010, 75 W bulbs were withdrawn from the market EU-wide
In September 2011, 60 W bulbs will be withdrawn from the market EU-wide
In September 2012, 15-45 W bulbs will be withdrawn from the market EU-wide
Energy efficiency
| Bulbs | Light current | LED |
|---|---|---|
| 25 W | 200 lm | Most available LEDs have an efficiency of 40-80 lm/W. The most efficient 1W LEDs currently attain 160 lm/W. |
| 40 W | 400 lm | |
| 60 W | 700 lm | |
| 75 W | 900 lm | |
| 100 W | 1400 lm | |
| 200 W | 3000 lm |
Service life
L70
As soon as the light current has fallen back to 70% of the original value, the light has reached the end of its useful service life.
The guaranteed service life of an LED is at present up to 60,000 hours.
The service life is greatly influenced by the operating temperature of the LED. It is therefore important when manufacturing LED lamps to achieve a correct balance between power output and cooling in order to ensure long life.
Color Rendering Index
The Color Rendering Index (CRI), also termed the Ra value, indicates how true the colors in the light are.
The maximum of 100 corresponds to natural daylight.
| Bulb | 100 |
| Fluorescent lamp | 70-90 |
| Halogen metal vapor lamp | 60-95 |
| Mercury vapor high-pressure lamp | 45 |
| Sodium vapor high-pressure lamp | 18-30 |

Color temperature
The color temperature is a measure of the color impression made by a light source; its unit is the Kelvin (K).
Warm/yellowish light colors have a low color temperature. The cooler/more blueish the light color, the higher the light temperature.
| Candle light | 1500 K |
| Sodium vapor lamp | 2000 K |
| Bulb (40W) | 2200 K |
| Bulb (100W) | 2680 K |
| Halogen lamp | 3000 K |
| Evening sunlight | 3400 K |
| Fluorescent lamp | 4000 K |
| Morning sunlight | 5000 K |
| Cloudy sky | 6500-7500 K |